

Ganciclovir triphosphate
Gancyclovir triphosphate, GCV-TP
Ganciclovir Triphosphate is the active metabolite of ganciclovir, an antiviral deoxyguanosine analog that is a strong inhibitor of viral DNA synthesis. Intracellular ganciclovir is phosphorylated to ganciclovir triphosphate, which is then incorporated into viral DNA to a greater extent than cellular DNA. Ganciclovir triphosphate incorporation into viral DNA results in a decrease and eventual cessation of DNA chain elongation.
Ganciclovir triphosphate is supplied as the triethylammonium salt in aqueous solution. This is the most stable form for triphosphates. The amount and concentration are written on the label.
For a quotation for larger quantities or for custom synthesis of any nucleoside mono, di or triphosphate, please inquire. Orders can be placed online, by telephone or by email
$184/1mg (1.1 µmole)
$478/2.5mg (2.8 µmole)
$850/5mg (5.5 µmole)
$1513/10mg (11 µmole)
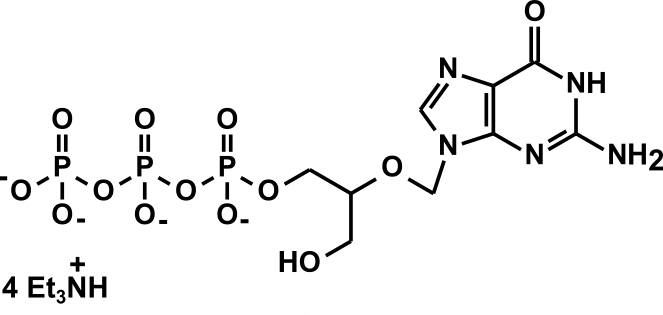
The 2D structure of Ganciclovir triphosphate is:
Selected references:
Biosynthetic ganciclovir triphosphate: its isolation and characterization from ganciclovir-treated herpes simplex thymidine kinase-transduced murine cells. Agbaria R, Candotti F, Kelley JA, Hao Z, Johns DG, Cooney DA, Blaese RM, Ford H Jr. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Nov 30;289(2):525-30. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6011.
Cytotoxicity and accumulation of ganciclovir triphosphate in bystander cells cocultured with herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase-expressing human glioblastoma cells. Rubsam LZ, Boucher PD, Murphy PJ, KuKuruga M, Shewach DS. Cancer Res. 1999 Feb 1;59(3):669-75.
Modifying gap junction communication in cancer therapy. Warawdekar UM, Jain V, Patel H, Nanda A, Kamble V. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Oct 15:103268. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2020.09.002. Online ahead of print. Abs: Pro-drug activation, a modality of cancer therapy leads to Ganciclovir triphosphate (GCV-TP) incorporation into newly synthesized DNA resulting in cell death.
Ganciclovir: an update of its use in the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. McGavin JK, Goa KL. Drugs. 2001;61(8):1153-83. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161080-00016. PMID: 11465876 Review. Abs: Ganciclovir is a nucleoside guanosine analogue which incorporates ganciclovir triphosphate (the active moiety) into DNA during elongation, thereby inhibiting viral replication. ...Oral ganciclovir monotherapy is as efficacious as sequential intravenous.
Hydroxyurea induces bystander cytotoxicity in cocultures of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase-expressing and nonexpressing HeLa cells incubated with ganciclovir. Gentry BG, Boucher PD, Shewach DS. Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;66(7):3845-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3660. Abs: Quantification of deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools showed that hydroxyurea decreased dGTP pools without significantly affecting ganciclovir triphosphate levels. ...These data suggest that the prolonged increase in the ganciclovir triphosphate.
Construction of plasmid vector pAFP-HSVtk-IRES2-EGFP and its effect on the cytotoxicity of ganciclovir to hepatocellular carcinoma. Lai Z, Qin Q, Yu B, Xie J, Gao R, Zhang T, Li C, Niu K, Xu J. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(12):2337-41. Abs: Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase phosphorylates ganciclovir to ganciclovir monophosphate, which is then converted to ganciclovir triphosphate by endogenous cellular nucleoside kinases.
Acyclic guanosine analogs inhibit DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon with very different potencies and have unique mechanisms of action. Ilsley DD, Lee SH, Miller WH, Kuchta RD. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 28;34(8):2504-10. doi: 10.1021/bi00008a014. Abs: Acyclovir triphosphate, ganciclovir triphosphate and penciclovir triphosphate inhibited DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon. Each of the compounds was polymerized by pol alpha, delta, and epsilon. Incorporation of acyclovir triphosphate.
Superior cytotoxicity with ganciclovir compared with acyclovir and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylthymine in herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase-expressing cells: a novel paradigm for cell killing. Rubsam LZ, Davidson BL, Shewach DS. Cancer Res. 1998 Sep 1;58(17):3873-82. Abs: Lower levels of ganciclovir triphosphate accumulated compared with araT triphosphate (araTTP) under conditions that induced < or =1 log cell kill (67 versus 1235 pmol/10(7) cells, respectively), and the half-life for the ganciclovir triphosphate.
Cytotoxicity and accumulation of ganciclovir triphosphate in bystander cells cocultured with herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase-expressing human glioblastoma cells. Rubsam LZ, Boucher PD, Murphy PJ, KuKuruga M, Shewach DS. Cancer Res. 1999 Feb 1;59(3):669-75. Abs: The ability of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase (HSV-TK)-expressing cells incubated with ganciclovir (GCV) to induce cytotoxicity in neighboring HSV-TK-negative (bystander) cells has been well documented. However, the proportion of araT-5'-triphosphate.
Toxicity assessment of intratumoral injection of the herpes simplex type I thymidine kinase gene delivered by retrovirus in patients with refractory cancer. Singh S, Cunningham C, Buchanan A, Jolly DJ, Nemunaitis J. Mol Ther. 2001 Aug;4(2):157-60. doi: 10.1006/mthe.2001.0430. Abs: Introduction of the herpes simplex type I thymidine kinase (HSV-TK) gene into tumor tissue, followed by ganciclovir, initiates a phosphorylation cascade that induces formation of a toxic ganciclovir triphosphate. Animal trials suggest that this ganciclovir.
Herpes simplex virus type 1 and human DNA polymerase interactions with 2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-triphosphate analogues. Kinetics of incorporation into DNA and induction of inhibition. Reardon JE. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19039-44. Abs: The relative efficiencies of the triphosphates of 9-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]guanine (acyclovir triphosphate, ACVTP), 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl] guanine (ganciclovir triphosphate, DHPGTP), and 2',3'-dideoxyguanosine (ddGTP) as substrates for the three.
Expression of the catalytic subunit (UL54) and the accessory protein (UL44) of human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase in a coupled in vitro transcription/translation system.
Cihlar T, Fuller MD, Cherrington JM.
Protein Expr Purif. 1997 Nov;11(2):209-18. doi: 10.1006/prep.1997.0781.
Abs: The in vitro-expressed enzyme resembles the purified HCMV DNA polymerase in its affinity for deoxynucleoside triphosphates as well as in its sensitivity to known inhibitors (cidofovir diphosphate, ganciclovir triphosphate, and foscarnet).
© Sierra Bioresearch, Copyright 1980-2022 All rights reserved.